Dec 20 2017 epidermis layer that helps maintain the shape of the stem. Keratinocytes are the predominant cells in the epidermis which are constantly generated in the basal lamina and go through maturation differentiation and migration to the.

Typical Anatomy Of A Leaf Structure A Leaf Contains A Waxy Cuticle An Download Scientific Diagram
It protects against water loss regulate gas exchange secretes metabolic compounds and especially in roots absorbs water.
Epidermis cell in plants tingkatan 3. Which provide support and flexibility to the stem. - Epidermal cell secrete waxy cuticle covering the outer surface of the leaf that will reduce water loss during transpiration. Layers of the epidermis.
Here hypotheses are tested that in such a cell mosaic growth is heterogeneous and changes with time and that this heterogeneity is not dependent on the cell cycle regulation per se. Inner walls of the guard cells face the aperture and are thicker than the outer layers. In young plants epidermis cells may secrete a waterproof cuticle.
Keratinocytes melanocytes and Langerhans cells. Epidermis is the outermost layer and is about 0051 mm in thickness depending on body part. The epidermis is made up of 95 keratinocytes but also contains melanocytes Langerhans cells Merkel cells and inflammatory cellsThe stratum basale is primarily made up of basal keratinocyte cells which can be considered the stem cells of the epidermis.
Quizlet flashcards activities and games help you improve your grades. The leaves and flowers of the homozygous acr41 and acr45 plants appeared normal in terms of both size and morphology When the plants were allowed to selfpollinate the siliques were shorter on the acr41 and acr45 plants than on the wildtype plants Figure 1de topIn addition the numbers of seeds in the developing siliques were reduced in the acr4 mutants Figure 1e. The skin contains multiple layers of cells.
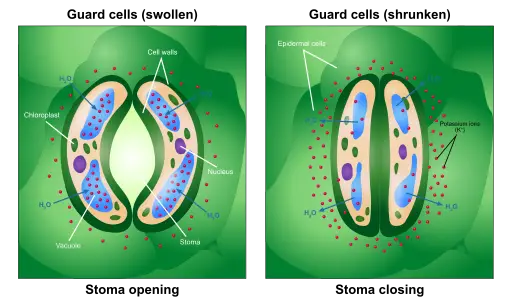
The cuticle however is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. The cells which surround the guard cells are known as subsidiary or accessory cells. SULIT 14 45512 45512 SULIT Diagram 63 Rajah 63 Diagram 64 Rajah 64 b Diagram 63 shows a rice plants in a paddy field.
Throughout the plant the L1 generates the epidermal tissue. Guard cells also have large vacuoles. In anthers EPI cells typically elongate into a columnar shape Kelliher.
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that make up the skin the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. Scant attention has been paid to steps in anther epidermal cell differentiation. Sel pengawal tisu epidermis EEppiiddeermrmisis B Root hair cell epidermal tissue EPmithpulur Sel rambut akar tisu epidermis C Tracheid vascular tissue Trakeid tisu vaskular D Companion cell ground tissue.
The wall of trichome may be silicified. Epidermal cell that covers both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf. Here it consists of a substance known as the cutin polymerized.
The epidermis of an expanding dicot leaf is a mosaic of cells differing in identity size and differentiation stage. However the skin is composed of tissues and performs mission-critical functions in the body. In plants leaves epidermal cells are located on the upper and lower part of the leaf where they form the upper and lower epidermis.
Other pigment like anthocyanin may occur in epidermal cells. Made up of parenchyma cells. The epidermis from the Greek ἐπιδερμίς meaning over-skin is a single layer of cells that covers the leaves flowers roots and stems of plantsIt forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment.
Nov 26 2020 A Guard cell epidermal tissue Diagram 3 shows a cross section of a dicot stem which experiences secondary growth. May 13 2016 Epidermis cells in general were highly vacuolated and large subcellular organelles such as the nucleus LD clusters non-green plastids and mitochondria were present together in large patches of cytoplasm. Aug 13 2020 Stratum Spinosum and Granulosum.
In older plants the epidermis may be absent replaced by bark. Tissues study guide by corylemay includes 60 questions covering vocabulary terms and more. Three main populations of cells reside in the epidermis.
Solitary and clustered LDs in a low or high proportion in a cell of a mature leaf could be related to biogenesis and function during. The guard cells of stomata that are specialized epidermal cells contain chloroplastids. The shoot epidermis plays important roles not only to protect plants from dehydration and pathogens but also to ensure their proper.
Dec 12 2016 The epidermal cells are devoid of chloroplasts. The epidermis serves several functions. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that.
Apr 27 2019 Generally in the big schema things of the human body the skin often does not strike as an organ. In plants this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis. Feb 25 2014 Land plants have evolved a single layer of epidermal cells which are characterized by mostly anticlinal cell division patterns formation of a waterproof coat called cuticle and unique cell types such as stomatal guard cells and trichomes.
The skin and their accessory structures such as hair glands and nails make up the integumentary system which provides the body with overall protection. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. Just inside the epidermis is.
- Much of water loss during transpiration in plants takes place through the stomata found in the leaf Figure below shows the structure of the. In some plants silicon may be deposited in the epidermal cells cither in the lumen or wall. The structure of the stomata consists of a kidney shaped epidermal cell with an opening in the center which is known as a pore.

English Leaf Anatomy Legend 1 Cuticle 2 Upper Epidermis 3 Palisade Mesophyll 4 Spongy Mesophyll 5 Lower Epidermi Parts Of A Leaf Vascular Plant Anatomy